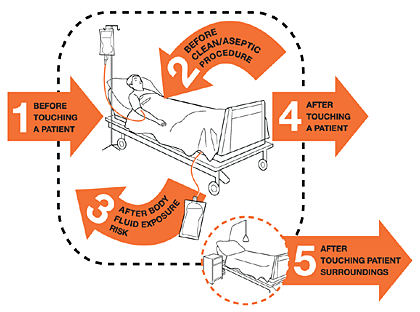
Hand hygiene has become nowadays one of the most heard behavioral activities. It is one of the most effective actions we should do to prevent the spread of the COVID 19 virus. Therefore alcohol hand sanitizers are an essential commodity.
The healthcare workers are not an exception.
However, adherence to cleaning hands with 70 percent alcohol hand sanitizers by healthcare workers requires promotion.
Simply, alcohol hand sanitizers should be made accessible at hand whenever necessary, most of the time at bedside of patients in hospitals.
Does alcohol-based hand rub sanitizers, when accessible, improve hand hygiene compliance among healthcare workers?
The answer is yes.
| Setting | Two ICUs and one general medical ward in a US hospital |
| Target audience | All healthcare workers |
| Study design | Six-month observational study |
| Intervention | One sanitizer per 4 bedsides initially and then one per each bedside was introduced. |
| Main outcome measure | Direct observation of handwashing randomized for the time of the day and bed location |
| Findings | The compliance rates improved from 19% to 41% with 1 dispenser per 4 beds and from 23% to 48% with 1 dispenser for each bed. |
| Conclusion | The introduction of sanitizers is associated with higher rates of handwashing compliance. |
| Journal reference | April 10, 2000, JAMA NETWORK; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/485276?resultClick=1 |
| Access | free access to the full article |
However, the finding is from an observational study.