Category: Corona virus
Is COVID 19 virus a living thing?
The COVID 19 virus has only a protein – RNA; it needs a living cell to produce its own copies.
How accurate our data on COVID 19?
The WHO’s estimate of the COVID 19 case fatality rate is 3.4 percent. According to John Ioannidis, the estimate is inaccurate. His reasoning is simple but comes from basic epidemiology principles; it should come from a random sample of a population and an accurate estimate of the number of infections in the host population. He uses Diamond Princess’s 700 passengers as the closest closed sample to calculate the estimate although this small population cannot be considered as a random sample. According to him, the case fatality rate of this population is 1 percent (7 deaths/700 passengers); this population is largely…
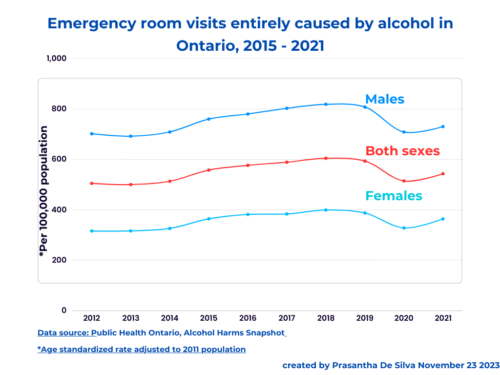
Interpreting rates: COVID-19
Source:https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd40299423467b48e9ecf6 This article, published in AlJazeera reminds me of my epidemiology lesson about interpreting rates. It is titled “why Italy’s coronavirus mortality rate is high”. I would begin with the order of questions that I would ask when I am confronted with the task of interpreting a rate. 1. Is there any artifact? yes; Italy’s denominator (number of infected cases due to their more restrictive case definition) is lower due to fewer number of testing from other countries such as South Korea and Germany (due to their more liberal case definitions). For example, as of March 15, South Korea has…
Interpreting rates: COVID-19
Source:https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594740fd40299423467b48e9ecf6 This article, from AlJazeera, reminds me of my epidemiology lesson about interpreting rates. Its heading reads as”why Italy’s coronavirus fatality rate is so high”. First about the concept of a “rate”. A rate has a numerator and a denominator = numerator/denomintor. We multiply the resulting value by either 1000, 10,000, 100,000, or even a million depending on the situation. In this situation, the denominator is the number of persons tested for the COVID 19 virus. Its numerator is the number of persons reported positive with the test. I would begin with the order of questions I would ask when…
Tracking COVID-19
February 11, 2020 March 17, 2020; after a month March 20, 2020: 3 days later March 24, 2020